Розуміння, встановлення та використання бази даних часових рядів InfluxDB 1.7
Переклад статті Understanding, installing and using the time series database InfluxDB 1.7
Introduction
При встановленні NetData, потужного інструменту моніторингу, часто задається питання: де зберігати та зберігати дані вимірювань?
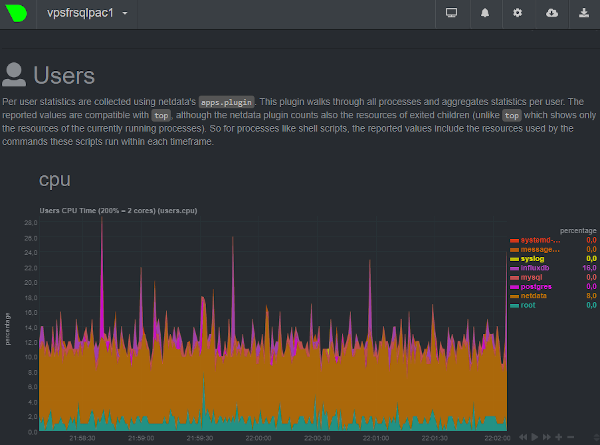
NetData дозволяє зберігати вимірювання у базі даних InfluxDB, базі даних часових рядів, за допомогою протоколу OpenTSDB (Open TimeSeries Database Protocol).
InfluxDB - це високопродуктивна база даних з ефективним стисненням, повністю написана на Go, вона не має зовнішніх залежностей. InfluxDB можна легко зв’язати з Grafana для цілей звітності. InfluxQL - це мова запитів для роботи з даними в базах даних InfluxDB і починаючи з версії 1.7, також введена мова Flux, яку можна активувати: Flux буде мовою в наступній великій версії InfluxDB, але, на жаль, остання сильно відрізняється від Мови SQL. Давайте подивимося архітектуру InfluxDB та способи її використання.
Архітектура
Термінологія: measurements, series, keys, values
Бази даних зберігають вимірювання (measurements). У наведеному нижче прикладі 2 вимірювання: netdata.users.mem.root та netdata.users.cpu.root.
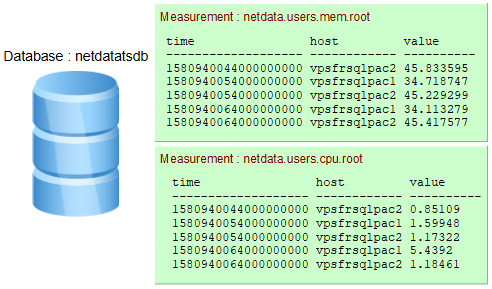
- Якщо під час вставки даних вимірювання не існує воно створюється.
Timeце час в Unix epoch(також називається “Unix time” або “POSIX time” або “Unix timestamp” - час в секундах з 1970-го року) але заданий в наносекундах:1580940454000000000↔02/05/2020 @ 10:07pm (UTC). Існує багато інструментів перетворення.
-
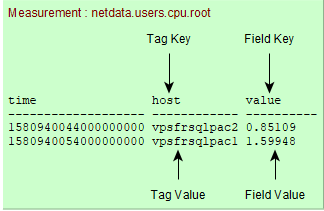
Ключі тегів (
Tag keys) можна визначити в одному рядку. У наведеному вище прикладі 1 ключ тегу:host -
У рядку можна визначити одне або декілька значень ключів поля (
field keys). У наведеному вище прикладі 1 ключ поля:value -
Ряди (
Series) - комбінація вимірювання/можливих ключів тегів:measurement, tag key1=value1, tag key2=value2 [,...]У вищенаведеному вимірюванні
netdata.users.cpu.rootє два ряди:netdata.users.cpu.root,host=vpsfrsqlpac1 netdata.users.cpu.root,host=vpsfrsqlpac2
InfluxDB Line protocol
Протокол рядків InfluxDB line protocol - це текстовий формат для написання точок на InfluxDB. Його формат дуже простий:
<measurement>[,<tag_key>=<tag_value>[,<tag_key>=<tag_value>]] <field_key>=<field_value>[,<field_key>=<field_value>] [<timestamp>]
За допомогою influx давайте створювати точки в базі даних netdatatsdb :
influxdb% influx -database 'netdatatsdb'> insert cpu_measurement,location=france,host=vpsfrsqlpac1 value=25.089878,description="low usage" 1580918550000000000
> insert cpu_measurement,location=germany,host=vpsfrsqlpac2 value=75.089878,description="high usage" 1580918550000000000
> select * from cpu_measurement;time description host location value
---- ----------- ---- -------- -----
1580918550000000000 high usage vpsfrsqlpac2 germany 75.089878
1580918550000000000 low usage vpsfrsqlpac1 france 25.089878
Коли мітку часу опущено, InfluxDB використовує локальну наносекундну мітку часу в UTC.
Теги або поля? Загальні рекомендації
Теги індексуються, а поля не індексуються. Запити повинні визначати, що зберігається як тег, а що як поле.
-
Зберігайте дані у тегах, якщо це метадані або якщо ви плануєте використовувати їх у запитах
GROUP BY. -
Важливо: значення тегів завжди інтерпретуються як strings. Тож якщо вони нам потрібні, щоб вони були чимось іншим, ніж рядок потрібно використовувати поля.
-
Зберігайте дані у полях, якщо вони використовуються з функціями SQL (
SUM,COUNT…). -
Не використовуйте однакові назви для тегу та поля.
-
Не кодуйте дані в іменах вимірювань та значеннях тегів, наскільки це можливо, це дозволить уникнути використання регулярних виразів. Наприклад використовувати
plot=1,region=northзамість
location=plot-1.northщоб уникнути таких регулярних виразів у запитах:
SELECT … FROM <measurement> WHERE location =~ /\.north$/
Бази даних, політика збереження та фрагменти(shards)
Для бази даних визначена політика збереження (retention policy), яка за замовченям є нескінченною (autogen). InfluxDB зберігає дані в фрагментарних групах (shard groups). Фрагментарні групи організовані за політикою збереження та зберігають дані з позначками часу, які потрапляють до певного часового інтервалу, який називається тривалістю фрагменту (shard duration).
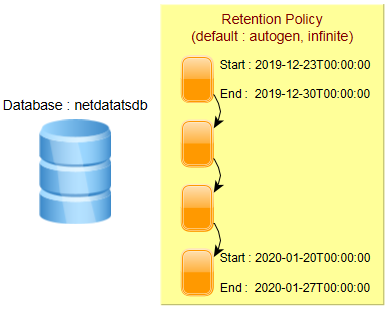
Тривалість фрагментів може бути визначена користувачем, інакше застосовуються наведені нижче значення за замовчуванням:
| Політика тривалості утримання (Retention policy duration) | Тривалість фрагментарної групи (Shard group duration) |
|---|---|
| < 2 days | 1 hour |
| >= 2 days and <= 6 months | 1 day |
| > 6 months | 7 days |
Тривалість групи фрагментів за замовчуванням добре працює в більшості випадків. Однак екземпляри з високою пропускною здатністю або тривалі роботи будуть корисними при використанні більшої тривалості фрагментарної групи. Рекомендації:
| Retention policy duration | Shard group duration |
|---|---|
| <= 1 day | 6 hours |
| > 1 day and <= 7 days | 1 day |
| > 7 days and <= 3 months | 7 days |
| > 3 months | 30 days |
| infinite | 52 weeks or longer |
Індексація в пам’яті та Time-Structured Merge Tree (TSM)
У версії 1.7 за замовчуванням механізм зберігання даних - це “In Memory Index”. Доступне нове сховище (TSI: Time Series Index), але воно не активоване за замовчуванням, про цей механізм зберігання йдеться в наступному параграфі.
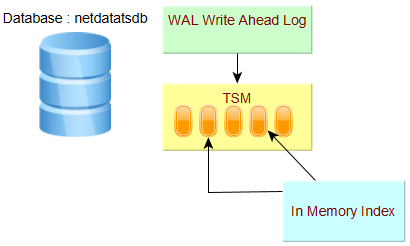
Кожна база даних має свою WAL (Write Ahead Log) та файли TSM.
- Сегменти WAL зберігають стислі блоки запису та видалення.
- Файли TSM зберігають стислі дані серії у стовпчастому форматі.
- Кеш - це представлення в пам’яті даних, що зберігаються в WAL. Він запитується під час виконання та об’єднується з даними, що зберігаються у файлах TSM.
- Індекс In-Memory - це спільний індекс для фрагментів, який забезпечує швидкий доступ до вимірювань, міток та серій.
Time Series Index (TSI)
Починаючи з версії 1.3, випускається двигун TSI. Він все ще вимкнений за замовчуванням, оскільки для існуючих баз даних необхідна міграція.
Механізм індексування In memory - TSM рушій показав обмеження для систем, що використовують мільйони серій, і високу потужність: до TSI інвертований індекс був структурою даних в пам’яті, побудованою під час запуску бази даних на основі даних у TSM. Використання пам’яті продовжувало зростати, оскільки створювалися нові часові ряди.
Новий індекс часових рядів (TSI) переміщує індекс до файлів на диску, файли відображаються у пам’яті. У цьому контексті операційна система обробляє найменш недавно використовувану (LRU least recently used) пам’ять. Фонові процедури виконуються постійно, щоб ущільнити індекс у більші та більші файли, щоб уникнути необхідності робити занадто багато об’єднань індексу під час запиту.
Підтримувані протоколи
Щодо передачі даних, InfluxDB підтримує наведені нижче протоколи, і можна визначити декількох слухачів:
- Collectd
- Graphite
- OpenTSDB
- Prometheus
- UDP
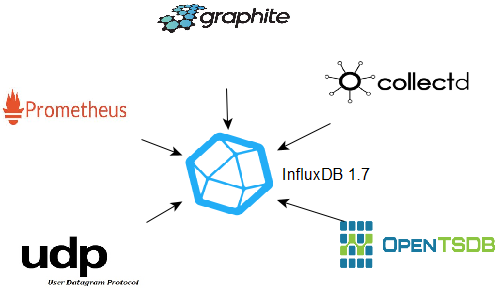
Починаючи з InfluxDB версії 2, фактично на стадії бета-тестування (лютий 2020 р.), Ці протоколи більше не підтримуватимуться безпосередньо: потрібно буде використовувати telegraf.
Installation
Пакет debian доступний для Ubuntu, але в цій статті, оскільки це некорнева установка, 64-бітні бінарні файли Linux версії 1.7.9 завантажуються з Веб-сайт InfluxDB.
Встановлення здійснюється користувачем influxdb в папці /opt/influxdata.
influxdb% cd /opt/influxdata
influxdb% wget https://dl.influxdata.com/influxdb/releases/influxdb-1.7.9_linux_amd64.tar.gz
influxdb% tar xvfz influxdb-1.7.9_linux_amd64.tar.gz
Отримана структура каталогів така:
/opt/influxdata/influxdb-1.7.9-1
|___etc
|___usr
|___var
Символічне посилання influxdb-1.7 створено для зручності використання та управління оновленнями.
influxdb% ln -fs influxdb-1.7.9-1 influxdb-1.7
The environment variable $IFXHOME is set to the root installation directory and the variable $IFXBIN to the directory where server and client binaries are located (influxd, influx…). The directory $IFXBIN is added to the environment variable $PATH.
influxdb% export IFXHOME=/opt/influxdata/influxdb-1.7
influxdb% export IFXBIN=$IFXHOME/usr/bin
influxdb% export PATH=$IFXBIN:$PATH
3 custom environment variables, $CFG, $LOG and $RUN, are created for the log, configuration and pid files directories :
influxdb% export CFG=/opt/influxdata/dba/srvifxsqlpac/cfg
influxdb% export LOG=/opt/influxdata/dba/srvifxsqlpac/log
influxdb% export RUN=/opt/influxdata/dba/srvifxsqlpac/run
That’s all, no need to define other variables for librairies and so on…
Preparing the configuration file
A template configuration file influxdb.conf is available in the directory $IFXHOME/etc
Create the configuration file from the template file and customize the values for the databases location (meta, data, wal) :
$CFG/srvifxsqlpac.conf
[meta]
dir = "/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/meta"
[data]
dir = "/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data"
wal-dir = "/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal"
If it is planned to use the language Flux, language that offers many new features (joins, pivot, external data sources access…), this one must be activated in the configuration file :
[http]
flux-enabled = true
The default port is 8086 and can be modified in the configuration file :
[http]
bind-address = ":8086"
Starting the server
To start the InfluxDB server, run influxd with the option -config giving the configuration file path :
nohup $IFXBIN/influxd -pidfile /tmp/srvifxsqlpac.pid -config $CFG/srvifxsqlpac.conf >> $LOG/srvifxsqlpac.log 2>&1 &
The option -pidfile is used to easier manage the shutdown procedure.
Connection to the server
Run the client influx to connect and execute InfluxQL commands :
influxdb% influxConnected to http://localhost:8086 version 1.7.9
InfluxDB shell version: 1.7.9> SHOW DATABASES;name: databases
name
----
_internal
Stopping the server
To stop the server :
influxdb% kill -s TERM <processid influxd>
influxdb% PIDFILE=$(cat $RUN/srvifxsqlpac.pid)
influxdb% kill -s TERM $PIDFILE
Managing databases, retention policies and shards
Creating a database
Easy : just run CREATE DATABASE
influxdb% influx> CREATE DATABASE netdatatsdb;
If the parameter retention-autocreate is not set to false in the configuration file, the default retention policy autogen set to infinite is activated in the database :
USE netdatatsdb;
SHOW RETENTION POLICIES;name duration shardGroupDuration replicaN default
---- -------- ------------------ -------- -------
autogen 0s 168h0m0s 1 true
Replication is set to 1. Replication is available only in the Enterprise Edition.
As the retention is infinite, the default shard group duration applied is 7 days (168 hours). The command SHOW SHARDS gives more details about the existing shards :
SHOW SHARDS;id database retention_policy shard_group start_time end_time expiry_time owners
-- -------- ---------------- ----------- ---------- -------- ----------- ------
15 netdatatsdb autogen 15 2019-12-23T00:00:00Z 2019-12-30T00:00:00Z 2019-12-30T00:00:00Z
22 netdatatsdb autogen 22 2020-01-06T00:00:00Z 2020-01-13T00:00:00Z 2020-01-13T00:00:00Z
26 netdatatsdb autogen 26 2020-01-13T00:00:00Z 2020-01-20T00:00:00Z 2020-01-20T00:00:00Z
47 netdatatsdb autogen 47 2020-01-20T00:00:00Z 2020-01-27T00:00:00Z 2020-01-27T00:00:00Z
58 netdatatsdb autogen 58 2020-02-03T00:00:00Z 2020-02-10T00:00:00Z 2020-02-10T00:00:00Z
Retention policies and shards
A retention policy autogen is created and predefined, obviously it can be modified creating or altering policies
CREATE RETENTION POLICY retention_infinite ON telegraf
DURATION inf REPLICATION 1 SHARD DURATION 52w DEFAULT;
USE telegraf;
SHOW RETENTION POLICIES;name duration shardGroupDuration replicaN default
---- -------- ------------------ -------- -------
autogen 0s 168h0m0s 1 false
retention_infinite 0s 8736h0m0s 1 true
The clause REPLICATION is mandatory in the CREATE statement even if the community OSS edition is used.
ALTER RETENTION POLICY autogen ON netdatatsdb SHARD DURATION 52w;
ALTER RETENTION POLICY autogen ON netdatatsdb DEFAULT;
USE netdatatsdb;
SHOW RETENTION POLICIES;name duration shardGroupDuration replicaN default
---- -------- ------------------ -------- -------
autogen 0s 8736h0m0s 1 true
About shards, the engine manages the pre-creation. The precreation can be controlled in the configuration file.
[shard-precreation]
# Determines whether shard pre-creation service is enabled.
enabled = true
# The interval of time when the check to pre-create new shards runs.
check-interval = "10m"
# The default period ahead of the endtime of a shard group that its successor group is created.
advance-period = "30m"
Querying and writing data
Metadata informations : measurements, series, tag and field keys
The command SHOW displays useful informations about metadata : measurements, series, tag keys, field keys…
Use SHOW MEASUREMENTS to list the measurements, regular expressions can be used :
SHOW MEASUREMENTS;…
netdata.users.vmem.alerta
netdata.users.vmem.apache
netdata.users.vmem.daemon
…
SHOW MEASUREMENTS WITH MEASUREMENT =~ /dbengines/;…
netdata.dbengines.cpu.influxd
netdata.dbengines.cpu.mysqld
netdata.dbengines.cpu.postgres
…
To list the series, SHOW SERIES :
SHOW SERIES;…
netdata.users.vmem.mcs,host=vpsfrsqlpac1
netdata.users.vmem.mcs,host=vpsfrsqlpac2
netdata.users.vmem.messagebus,host=vpsfrsqlpac1
netdata.users.vmem.messagebus,host=vpsfrsqlpac2
netdata.users.vmem.mongodb,host=vpsfrsqlpac1
…
SHOW SERIES FROM "netdata.users.cpu.postgres";key
---
netdata.users.cpu.postgres,host=vpsfrsqlpac1
netdata.users.cpu.postgres,host=vpsfrsqlpac2
SHOW SERIES FROM "netdata.users.cpu.postgres"
WHERE host = 'vpsfrsqlpac1';key
---
netdata.users.cpu.postgres,host=vpsfrsqlpac1
SHOW SERIES FROM "netdata.users.cpu.postgres"
WHERE host !~ /vpsfrsqlpac1/;key
---
netdata.users.cpu.postgres,host=vpsfrsqlpac2
Tag and field keys can be also listed with SHOW commands, including the distinct values from tag keys :
SHOW TAG KEYS FROM "cpu_measurement";name: cpu_measurement
tagKey
------
host
location
SHOW TAG VALUES FROM "cpu_measurement"
WITH KEY=location;name: cpu_measurement
key value
--- -----
location france
location germany
SHOW FIELD KEYS FROM "cpu_measurement";name: cpu_measurement
fieldKey fieldType
-------- ---------
description string
value float
Queries
Specify the precision rfc3339 to convert the Unix timestamps to human-readable time.
PRECISION rfc3339
SELECT MEAN(value) AS mean_value
FROM "netdata.users.cpu.postgres"
WHERE time > '2020-01-16T02:30:00.000Z' AND time < '2020-01-16T03:30:00.000Z'
AND host = 'vpsfrsqlpac1'
GROUP BY time(10s)name: netdata.users.cpu.postgres
time mean_value
---- ----------
2020-01-16T02:41:10Z 1.68414
2020-01-16T02:41:20Z 1.19909
2020-01-16T02:41:30Z 1.17531
Subqueries are allowed.
Numerous InfluxQL functions are available.
Writing data
Enforcing data types
Let’s write a point :
INSERT cpu_measurement,location=france,host=vpsfrsqlpac1 cpupct=32.887384,slot=1
SELECT * FROM cpu_measurementname: cpu_measurement
time cpupct host location slot
---- ------ ---- -------- ----
1581037980496337504 32.887384 vpsfrsqlpac1 france 1
The column type is automatically defined when inserting the first point :
SHOW FIELD KEYS FROM cpu_measurementname: cpu_measurement
fieldKey fieldType
-------- ---------
cpupct float
slot float
The datatype of the column slot has been automatically defined to float. If you want to set the exact datatype : data type integer for the column slot, add i after the value when inserting the first point. For boolean data types, be sure to write true or false without quotes or double quotes:
INSERT cpu_measurement,location=france,host=vpsfrsqlpac1 cpupct=32.887384,slot=1i,active=true
SHOW FIELD KEYS FROM cpu_measurementname: cpu_measurement
fieldKey fieldType
-------- ---------
active boolean
cpupct float
slot integer
Setting the right data type reduces memory and space consumptions and it enforces data integrity : wrong values will be rejected
INSERT cpu_measurement,location=france,host=vpsfrsqlpac1 cpupct=32.887384,slot=1.121212ERR: {"error":"partial write: field type conflict: input field \"slot\" on measurement \"cpu_measurement\" is type float,
already exists as type integer dropped=1"}
Bulk import
Bulk import is very easy, just create a file with the header containing DDL/DML CONTEXT-DATABASE clauses and then the lines in InfluxDB Line protocol:
prices.txt
# DDL
CREATE DATABASE finance
# DML
# CONTEXT-DATABASE: finance
prices,type=NSDQ open=10.62,high=10.82,low=10.62,clot=10.65,capit=3.09 1580918400
prices,type=NSDQ open=10.65,high=10.95,low=10.64,clot=10.59,capit=3.09 1581004800
The database can already exists, otherwise it is created. The DML specifies which database to use.
The client influx is executed to import :
influxdb% influx -import -path=prices.txt -precision=s2020/02/07 13:12:53 Processed 1 commands
2020/02/07 13:12:53 Processed 1249 inserts
2020/02/07 13:12:53 Failed 0 inserts
influxdb% influx -database finance -precision rfc3339select * from prices limit 2name: prices
time capit clot high low open type
---- ----- ---- ---- --- ---- ----
2020-02-05T16:00:00Z 3.09 10.65 10.82 10.62 10.62 NSDQ
2020-02-06T16:00:00Z 3.09 10.59 10.95 10.64 10.65 NSDQ
SELECT INTO
Data and queries results can be copied, even in a cross database context, with the SELECT INTO statement.
USE finance;
SELECT * INTO mydb..prices from prices;name: result
time written
---- -------
0 2
Continuous queries can automate SELECT INTO statements in order to compute/aggregate results and so on… But this functionality is not covered here in this introduction, it is a chapter apart, there are many things to point out.
Listeners and data ingestion
InfluxDB 1.x supports natively the protocols below for data ingestion :
- Graphite
- OpenTDS
- CollectD
- Prometheus
- UDP
With InfluxDB V2, it will not be possible anymore, telegraf will be mandatory for feeding the InfluxDB database through these protocols.
Just one example here : Netdata sends its metrics with the protocol OpenTDS, so an OpenTDS listener (port 4242) is defined in the InfluxDB server configuration file. A database is attached to the listener, it will be created if it does not exist. Multiple listeners can be defined.
$CFG/srvifxsqlpac.conf
[[opentsdb]]
enabled = true
bind-address = ":4242"
database = "netdatatsdb"
The InfluxDB server OpenTDS port is specified in the Netdata configuration file :
netdata.conf
[backend]
# host tags =
enabled = yes
data source = average
type = opentsdb
destination = tcp:vpsfrsqlpac1:4242
prefix = netdata
update every = 10
buffer on failures = 10
timeout ms = 20000
Visualizing data
Chronograf
A visualization tool is available for download : Chronograf. The installation is very easy.
influxdb% cd /opt/influxdata
influxdb% wget https://dl.influxdata.com/chronograf/releases/chronograf-1.7.16_linux_arm64.tar.gz
influxdb% tar xvfz chronograf-1.7.16_linux_arm64.tar.gz
influxdb% ln -fs chronograf-1.7.16-1 chronograf-1.7
To start Chronograf on port 8087 :
influxdb% cd /opt/influxdata
influxdb% nohup ./chronograf-1.7/usr/bin/chronograf --port 8087 --influxdb-url=http://vpsfrsqlpac1:8086 \
--bolt-path $CFG/chronograf/chronograf.db >> /dev/null 2>> $LOG/chronograf.log &time="2020-02-06T15:06:51+01:00" level=info msg="Serving chronograf at http://[::]:8087" component=server
The bolt database (--bolt-path), created when running Chronograf for the first time, store dashboards definitions…
The tool is very easy to use and intuitive.
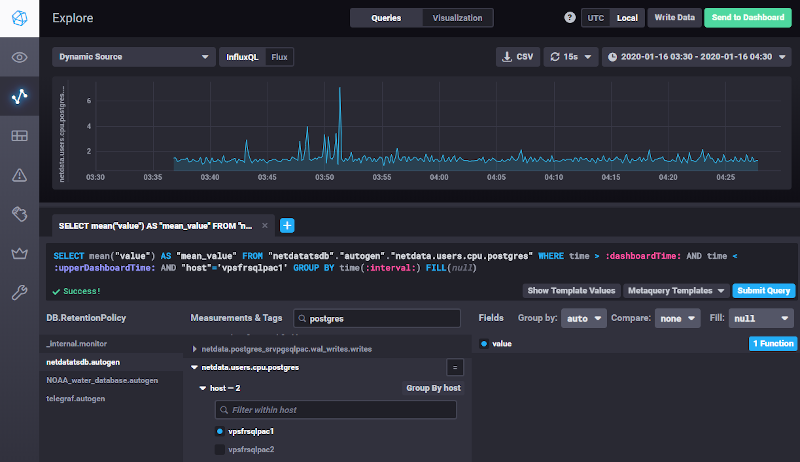
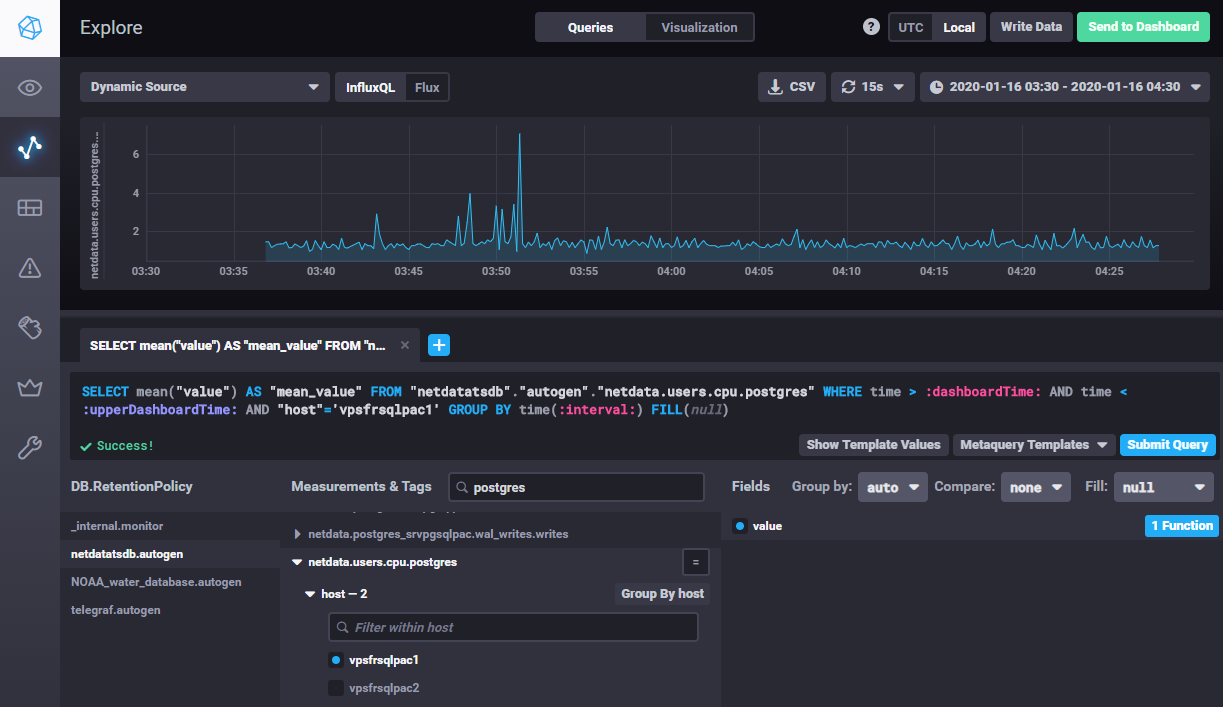
Starting InfluxDB version 1.7.x and if the language Flux is enabled in the configuration file (flux-enabled = true), both InfluxQL and Flux languages are available in Chronograf : menu buttons allow to switch from one to another. This functionality will be helpful when preparing the migration to InfluxDB v2, InfluxQL will be indeed removed in this version and Flux will be the unique language.
Further notice : starting version 2.0, Chronograf functionalities are fully integrated in InfluxDB, it will not be anymore a separate standalone tool.
Grafana
Grafana easily integrates dashboards with InfluxDB as a data source. In the menu, select ConfigurationData Sources, click the button “Add Data Source” and then choose “InfluxDB”. Fill the datasource connection informations (http://<hostname>:<port InfluxDB>…) and that’s all, then building dashboards is very intuitive.
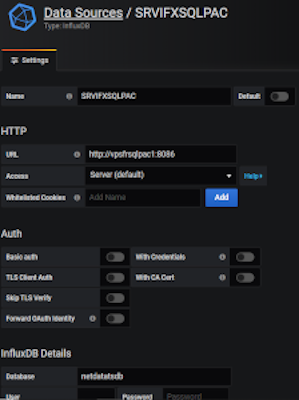
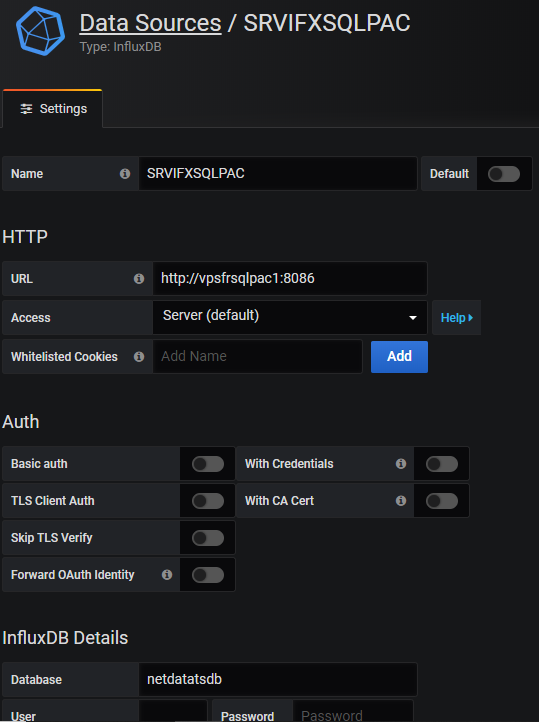
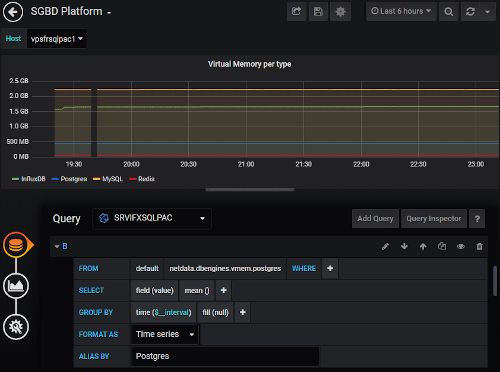
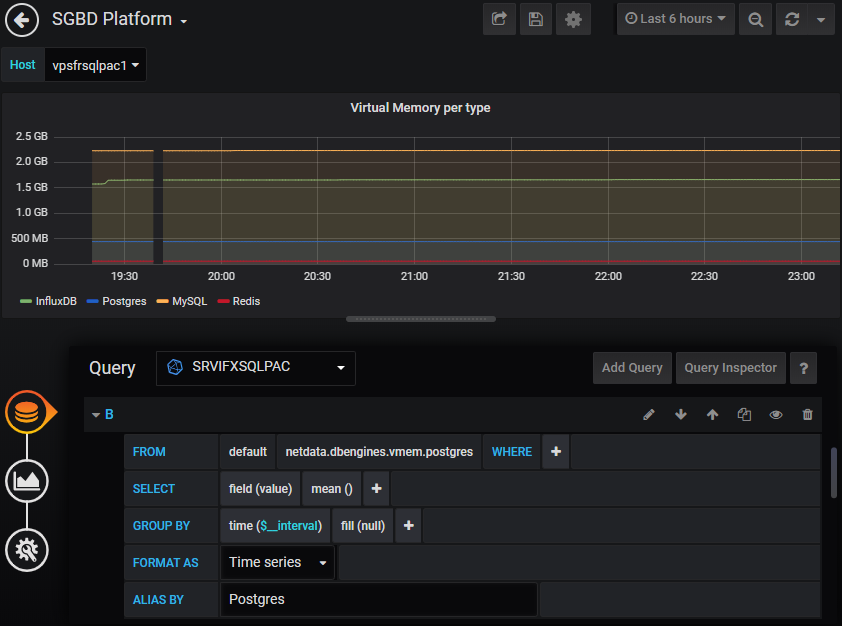
The plugin for the Flux language is in beta phase but available : Flux (InfluxDB) DataSource plugin. It requires Grafana 6.4 and onwards versions.
Statistics and configuration
Use the command SHOW STATS to consult statistics. Without arguments, all statistics are displayed, except the in memory index size.
In Memory index size
SHOW STATS FOR 'indexes'name: indexes
memoryBytes
-----------
5438060
Statistics per database
SHOW STATS FOR 'database'name: database
tags: database=_internal
numMeasurements numSeries
--------------- ---------
13 147
name: database
tags: database=netdatatsdb
numMeasurements numSeries
--------------- ---------
2727 4441
Getting database size is not trivial, one can use SHOW STATS FOR 'shard' but the output is not easy, shards are not ordered by database name :
SHOW STATS FOR 'shard';name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, engine=tsm1, id=15, indexType=inmem, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/15,
retentionPolicy=autogen, walPath=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal/netdatatsdb/autogen/15
diskBytes fieldsCreate seriesCreate writeBytes writePointsDropped writePointsErr writePointsOk writeReq writeReqErr writeReqOk
--------- ------------ ------------ ---------- ------------------ -------------- ------------- -------- ----------- ----------
36094696 0 2973 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, engine=tsm1, id=22, indexType=inmem, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/22,
retentionPolicy=autogen, walPath=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal/netdatatsdb/autogen/22
diskBytes fieldsCreate seriesCreate writeBytes writePointsDropped writePointsErr writePointsOk writeReq writeReqErr writeReqOk
--------- ------------ ------------ ---------- ------------------ -------------- ------------- -------- ----------- ----------
17649537 0 3422 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, engine=tsm1, id=26, indexType=inmem, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/26,
retentionPolicy=autogen, walPath=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal/netdatatsdb/autogen/26
diskBytes fieldsCreate seriesCreate writeBytes writePointsDropped writePointsErr writePointsOk writeReq writeReqErr writeReqOk
--------- ------------ ------------ ---------- ------------------ -------------- ------------- -------- ----------- ----------
110735177 0 3691 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, engine=tsm1, id=47, indexType=inmem, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/47,
retentionPolicy=autogen, walPath=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal/netdatatsdb/autogen/47
diskBytes fieldsCreate seriesCreate writeBytes writePointsDropped writePointsErr writePointsOk writeReq writeReqErr writeReqOk
--------- ------------ ------------ ---------- ------------------ -------------- ------------- -------- ----------- ----------
28286352 0 3577 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, engine=tsm1, id=58, indexType=inmem, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/58,
retentionPolicy=autogen, walPath=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal/netdatatsdb/autogen/58
diskBytes fieldsCreate seriesCreate writeBytes writePointsDropped writePointsErr writePointsOk writeReq writeReqErr writeReqOk
--------- ------------ ------------ ---------- ------------------ -------------- ------------- -------- ----------- ----------
46062999 234 3294 0 0 0 5699051 7092 0 7092
Or a query can be issued directly in the database _internal to filter the database name.
USE _internal;
SELECT last("diskBytes")
FROM "monitor"."shard"
WHERE ("database" =~/netdatatsdb/)
AND time >= now() -1m
GROUP BY "database", "path" fill(null);name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/15
time last
---- ----
1581030800000000000 36094696
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/22
time last
---- ----
1581030800000000000 17649537
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/26
time last
---- ----
1581030800000000000 110735177
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/47
time last
---- ----
1581030800000000000 28286352
name: shard
tags: database=netdatatsdb, path=/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data/netdatatsdb/autogen/58
time last
---- ----
1581030800000000000 44106795
Statistics per input plugins (listeners)
When listeners are setup for data ingestion (opentsdb, graphite, udp…), statistics per listener can be displayed : in the example below, opentsdb on port 4242 for data ingestion coming from netdata.
SHOW STATS for 'opentsdb';name: opentsdb
tags: bind=:4242
batchesTx batchesTxFail connsActive connsHandled droppedPointsInvalid httpConnsHandled pointsTx tlBadFloat tlBadLine tlBadTag tlBadTime
--------- ------------- ----------- ------------ -------------------- ---------------- -------- ---------- --------- -------- ---------
7542 0 1 1 0 0 6063674 0 0 0 0
tlBytesRx tlConnsActive tlConnsHandled tlPointsRx tlReadErr
--------- ------------- -------------- ---------- ---------
462091571 1 1 6063674 0
Running queries
Unoptimized queries may have unexpected behaviours in the InfluxDB engine (CPU…), use SHOW QUERIES and KILL QUERY to kill high consuming resources queries :
SHOW QUERIES
qid query
--- -----
690 SELECT mean(value) AS mean_value FROM netdatatsdb.autogen."netdata.users.cpu.postgres" WHERE time > '1900-01-16T02:30:00.000Z' AND time < '2020-01-16T03:30:00.000Z' AND host = 'vpsfrsqlpac1' GROUP BY time(10s)
database duration status
-------- -------- ------
netdatatsdb 8m2s runningKILL QUERY 690;
Configuration
To view the current settings :
SHOW DIAGNOSTICS;name: build
Branch Build Time Commit Version
------ ---------- ------ -------
1.7 23bc63d43a8dc05f53afa46e3526ebb5578f3d88 1.7.9
name: config
bind-address reporting-disabled
------------ ------------------
127.0.0.1:8088 false
name: config-coordinator
log-queries-after max-concurrent-queries max-select-buckets max-select-point max-select-series query-timeout write-timeout
----------------- ---------------------- ------------------ ---------------- ----------------- ------------- -------------
0s 0 0 0 0 0s 10s
name: config-cqs
enabled query-stats-enabled run-interval
------- ------------------- ------------
true false 1s
name: config-data
cache-max-memory-size cache-snapshot-memory-size cache-snapshot-write-cold-duration compact-full-write-cold-duration
--------------------- -------------------------- ---------------------------------- --------------------------------
1073741824 26214400 10m0s 4h0m0s
dir max-concurrent-compactions max-index-log-file-size max-series-per-database max-values-per-tag series-id-set-cache-size
--- -------------------------- ----------------------- ----------------------- ------------------ ------------------------
/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/data 0 1048576 1000000 100000 100
wal-dir wal-fsync-delay
------- ---------------
/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/wal 0s
name: config-httpd
access-log-path bind-address enabled https-enabled max-connection-limit max-row-limit
--------------- ------------ ------- ------------- -------------------- -------------
:8086 true false 0 0
name: config-meta
dir
---
/sqlpac/influxdb/srvifxsqlpac/meta
name: config-monitor
store-database store-enabled store-interval
-------------- ------------- --------------
_internal true 10s
name: config-opentsdb
enabled bind-address database retention-policy batch-size batch-pending batch-timeout
------- ------------ -------- ---------------- ---------- ------------- -------------
true :4242 netdatatsdb 1000 5 1s
name: config-precreator
advance-period check-interval enabled
-------------- -------------- -------
30m0s 10m0s true
name: config-retention
check-interval enabled
-------------- -------
30m0s true
name: config-subscriber
enabled http-timeout write-buffer-size write-concurrency
------- ------------ ----------------- -----------------
true 30s 1000 40
name: network
hostname
--------
vpsfrsqlpac1
name: runtime
GOARCH GOMAXPROCS GOOS version
------ ---------- ---- -------
amd64 2 linux go1.12.6
name: system
PID currentTime started uptime
--- ----------- ------- ------
1382 2020-02-06T23:37:16.912800481Z 2020-02-06T18:20:27.149884796Z 5h16m49.762915685s
Conclusion
InfluxDB is a time series database with interesting performances and functionalities.
- Easy ingestion, natively or through common protocols (OpenTSDB, Graphite…).
- Queries SQL Like.
- Easy reporting and visualization with Grafana or Chronograf.
A useful functionality has not been covered in this introduction : the continuous queries. Too many things to point out.
Important note, actually in beta version (February 2020), InfluxDB v2 will be released soon and maybe the migration will not be so easy :
- The InfluxQL language is replaced by the Flux language in this release. Even if it contains interesting new features compared to InfluxQL (joins, pivots, access to external data…), the Flux language is more a no-SQL language not so obvious to learn.
- Native support for the protocols Graphite, OpenTSDB… is removed. The tool telegraf will be mandatory.
- Continuous queries are replaced by tasks.
https://grafana.com/products/cloud/
https://www.influxdata.com/get-influxdb/
Analysis of the Storage Mechanism in InfluxDB
https://www.sqlpac.com/en/documents/influxdb-migration-procedure-v1-v2.html
https://youtu.be/zTek40zc9Cg
https://youtu.be/-3dDD4KmCAM